Introduction¶
Intel’s Multi-OS Engine Technology Preview lets you use Java* capabilities to develop native mobile applications for Apple iOS* and Android* devices providing the native look, feel and performance. This technology provides a stand-alone plug-in that integrates into Android Studio* on Windows* and/or Apple macOS development machines.
An application starts as an Android project in Android Studio. The Multi-OS Engine configures the project to build and run as an iOS app on the iOS simulator that you can invoke from Android Studio or on a real device.

The key features of Multi-OS Engine are:
- Java support on iOS devices.
- Developing iOS apps in Java instead of Apple Objective-C*.
- Direct access to platform-specific UI components for either of the supported platforms.
- Native multithreading support.
- Debugging apps on real devices or the iOS simulator integrated with Android Studio.
- Running/deploying apps from Apple App Store*.
To get started, follow the instructions in the Getting Started section.
Multi-OS Engine Architecture Overview¶
Multi-OS Engine Runtime is based on the modern Android ART*, which is the runtime component of Android that runs Java apps.
ART has a list of features that provide optimal performance for apps on iOS devices:
- Ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation, which can improve app performance.
- Use of the same Java runtime libraries as Android, which simplify cross-platform app development.
- Enhanced memory management and garbage collection.
A compiled Multi-OS Engine app contains the following components:
- Compiled Java sources.
- Resources.
- Standard (iOS) library bindings.
- Third party native libraries and bindings.
- Nat/J native library for the Java to native binding that enables the implementation of native classes and functions in pure Java and makes them available to the native side.
- The specialized ART virtual machine (VM) with Multi-OS Engine ART enhancements.
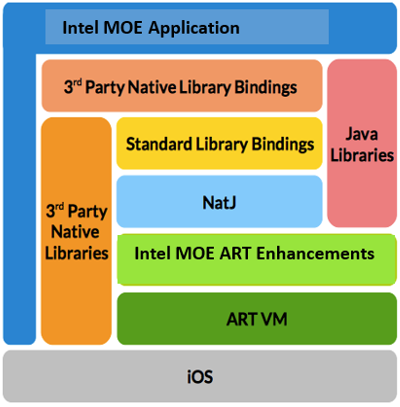
When an iOS app launches, it starts the ART VM and executes the pre-compiled code on it.
iOS* Development Workflow with the Multi-OS Engine¶
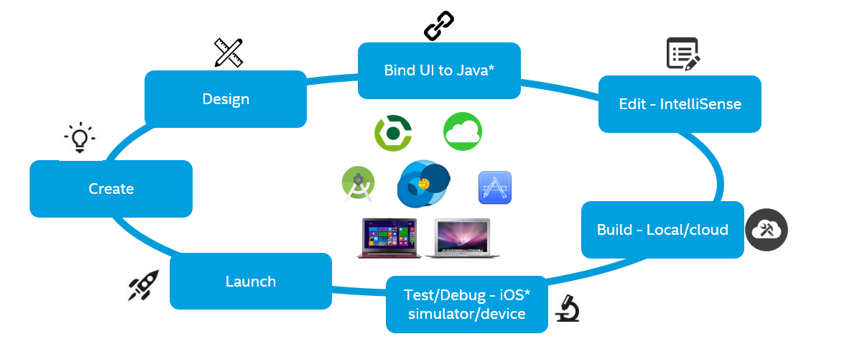
- Create an Android project in Android Studio. To configure your iOS app, add a new configuration Multi-OS Engine Project. Other steps below explain only the creation of iOS* App with Multi-OS Engine, and assume you are aware of the build process of an Android app in Android Studio.
- Design a User Interface (UI) for iOS in Apple Xcode*.
- Bind UI to Java* using the NatJ runtime libraries.
- Android Studio is equipped with the Intellisense capabilities to bind the action handlers to the UI elements for iOS.
- A local build is supported on macOS development machines where iOS Simulators can be invoked. For Windows* development systems, cloud build is supported.
- iOS applications can be run on the Simulator integrated into Android Studio by the Multi-OS Engine configuration or directly on the device itself using USB debugging.
- Launch your app by publishing and downloading it from the Apple App Store* for iOS* devices or the Google Play Store* for Android devices.
- Reiterate the process. Your goal is to reuse as much code as possible between these two apps.
